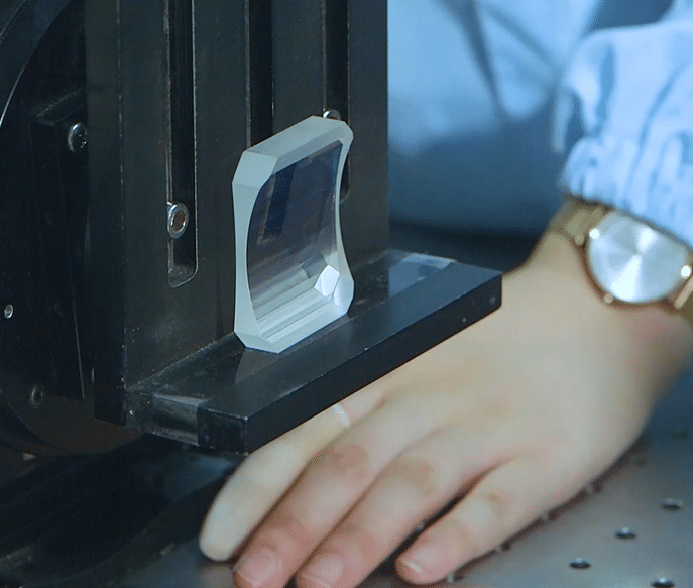
Popular Bk7 Diameter 74mm Anti-reflection Coating Optical Glass Plano-convex Cylindrincal Lens
Include
• Correcting astigmatism in imaging systems.
• Adjusting the height of an image.
• Creating circular, rather than elliptic, laser beams.
• Compressing images to one dimension.
The focal length of a lens is determined when the lens is focused at infinity. Lens focal length tells us the angle of view—how much of the scene will be captured—and the magnification—how large individual elements will be. The longer the focal length, the narrower the angle of view and the higher the magnification.
Cylindrical lenses find use in a wide range of industries. Common applications for cylindrical optical lenses include detector lighting, bar code scanning, spectroscopy, holographic lighting, optical information processing and computer technology. Because applications for these lenses tend to be highly specific, you may need to order custom cylindrical lenses to achieve the desired results.
Specifications
Standard Cylindrical PCX Lens:
Positive cylindrical lenses are ideal for applications requiring magnification in one dimension. A typical application is to use a pair of cylindrical lenses to provide anamorphic shaping of a beam. A pair of positive cylindrical lenses can be used to collimate and circularize the output of a laser diode. Another application possibility would be to use a single lens to focus a diverging beam onto a detector array. These H-K9L Plano-Convex Cylindrical lenses are available uncoated or with one of three anti-reflection coatings: VIS (400-700nm); NIR (650-1050nm) and SWIR(1000-1650nm).
Standard Cylindrical PCX Lens:
| Material | H-K9L (CDGM) |
| Design Wavelength | 587.6nm |
| Dia. tolerance | +0.0/-0.1mm |
| CT tolerance | ±0.2mm |
| EFL Tolerance | ±2 % |
| Centration | 3~5arcmin. |
| Surface Quality | 60-40 |
| Bevel | 0.2mmX45° |
| Coating | AR coating |
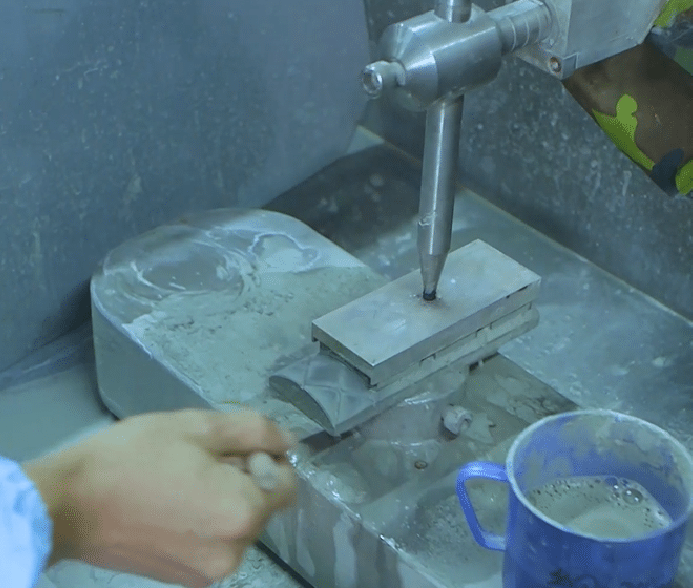
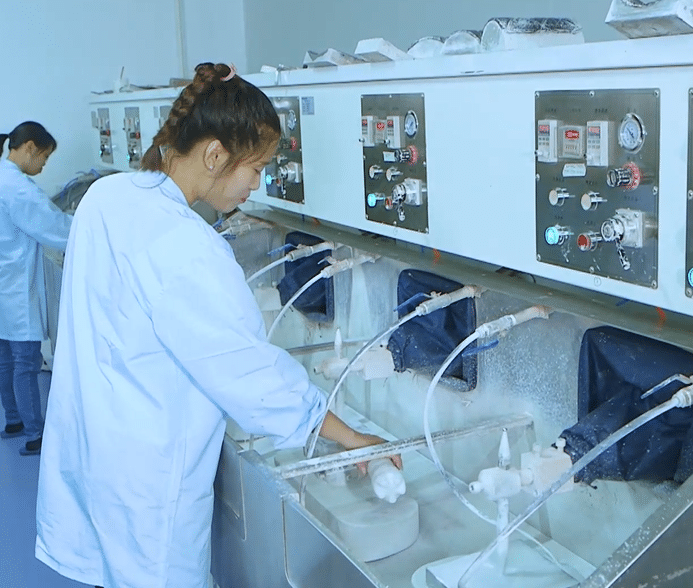
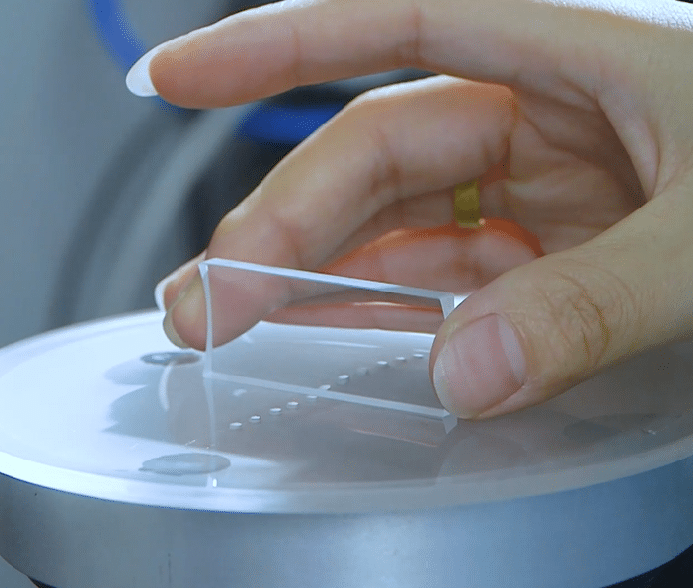
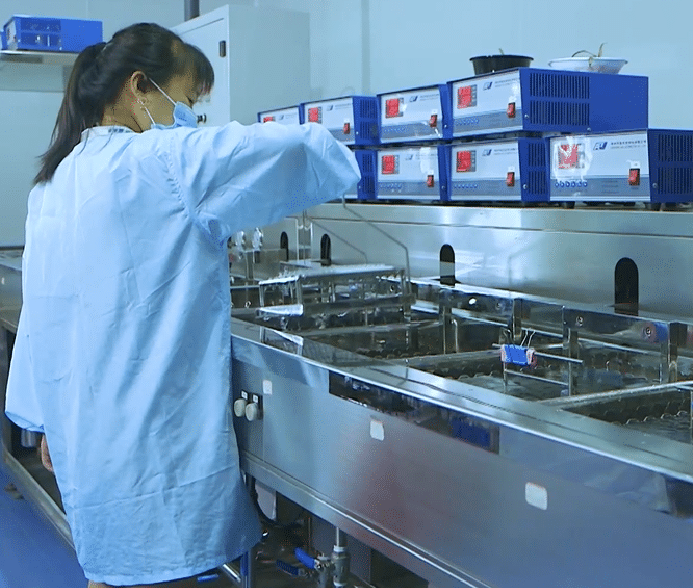
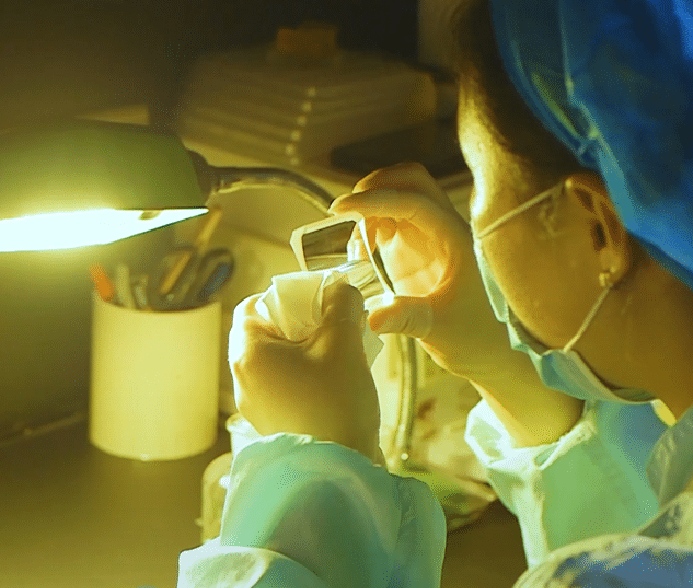
Workshop Show