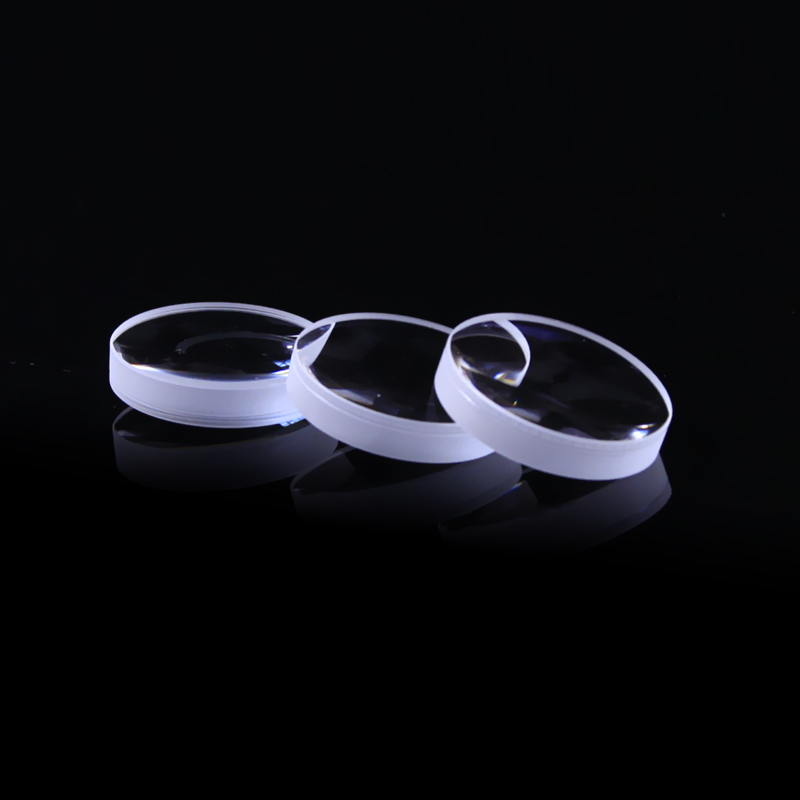
Precision Polished Aspheric Lenses
Small aspheric glass lenses can be made by molding, which allows cheap mass production. Due to their low cost and good performance, molded aspheres are commonly used in inexpensive consumer cameras, camera phones, and CD players.They are also commonly used for laser diode collimation, and for coupling light into and out of optical fibers.
Larger aspheres are made by grinding and polishing. Lenses produced by these techniques are used in telescopes, projection TVs, missile guidance systems, and scientific research instruments. They can be made by point-contact contouring to roughly the right form which is then polished to its final shape. In other designs, such as the Schmidt systems, the aspheric corrector plate can be made by using a vacuum to distort an optically parallel plate into a curve which is then polished "flat" on one side. Aspheric surfaces can also be made by polishing with a small tool with a compliant surface that conforms to the optic, although precise control of the surface form and quality is difficult, and the results may change as the tool wears.
| Place of Origin: | Jiangsu,China, 2 hours by car from Shanghai |
| Brand Name: | DG Optics |
| Material | BK7 ,Fused silica, Sapphire ,CaF2, ZnSe, Si, Ge |
| Coating | UV, IR , SWIR, NIR ,VIS |
| Structure: | ASPHERICAL |
| Surface Quality: | 40/20, 20/10, 5/0 |
| Diameter | 0.5-600mm |
| Clear Aperture | Over 90% |
| Chamfer | 0.1-0.3 mm*45 degree |
| Focal Length Tolerance | +/-1% |
| Irregularity (P-V) @ 632.8nm: | λ/4 |




 Other lens types :
Other lens types :